Find out all the details about the INSS! Surely you've heard of this body, but fully understanding how it works is crucial. The INSS plays a vital role in making social security benefits possible for Brazilian workers, especially retirement. Given the obligation and legal provision, paying this tax is part of the routine for both companies and employees.
In this context, companies must pay attention to the collection and payroll INSS calculationThe payroll deduction is an essential labor obligation. However, due to the numerous guidelines and rules involved, many workers may come across the payroll deduction without fully understanding its reasoning. This article aims to clear up any doubts on the subject, covering important details to provide a comprehensive understanding of the INSS and its impacts on both employers and employees.
What is the INSS and how is it relevant to entrepreneurs?
How important is the INSS for companies?

The INSS plays a fundamental role for companies, and is of great importance for a number of reasons. One of the main ones is its direct relationship with the labor and social security obligations that companies have towards their employees. The INSS, or National Social Security Institute, is responsible for providing social security benefits, such as retirement, sick pay, maternity pay and others, guaranteeing social protection for workers. social protection for workers.
In addition, the INSS directly influences companies' financial management, since social security contributions are levied on the payroll. Understanding and complying with the rules and regulations relating to INSS is essential to avoiding legal penalties and ensuring that social security contributions are paid correctly.
The relationship between companies and the INSS also stands out for its shared responsibility for maintaining the social security system. By paying contributions, companies contribute to the sustainability of the system, ensuring that workers have access to social security benefits when necessary. Therefore, the importance of the INSS for companies goes beyond legal issues, encompassing financial and social aspects that have a direct impact on the corporate environment.
How to calculate social security contributions for companies?
INSS Patronal
Companies are obliged to contribute a percentage of their payroll to the INSS Patronal. This rate varies according to the company's economic activity.
Third parties
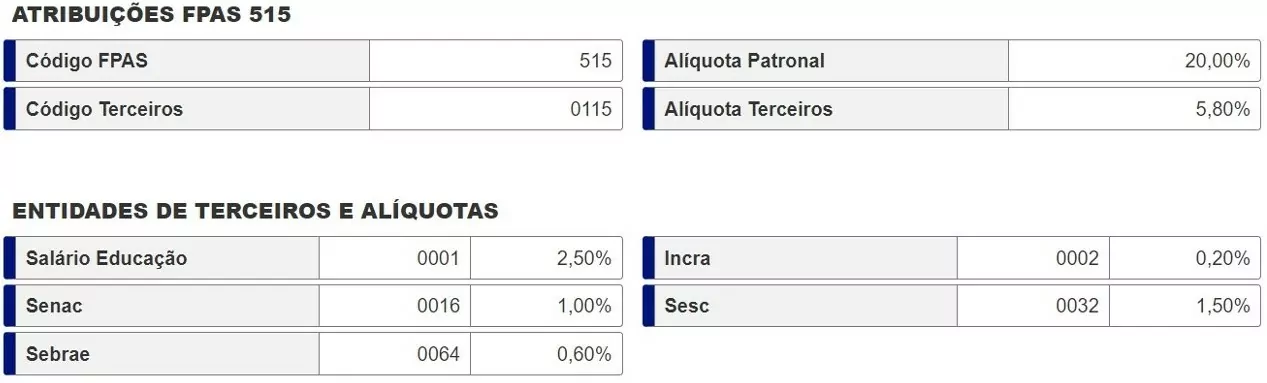
In addition to INSS Patronal, some companies also contribute to third parties, such as Sistema S (Senai, Sesi, Senac, etc.), INCRA, RAT and salário-educação.
Family Allowance and Maternity Allowance
These are additional contributions that vary according to payroll.
INSS Table 2024
Contribution salary (monthly income) x Progressive rates
- Up to R$ 1,412: 7.5%
- From R$ 1,412.01 to R$ 2,666.68: 9%
- From R$ 2,666.69 to R$ 4,000.03: 12%
- From 4,000.04 to R$ 7,786.02: 14%
Comments:
Rates
The rates shown are examples and may vary depending on the company's activity. We recommend checking current legislation.
Basis of calculation
Some contributions have specific calculation bases, and this example simplifies them to illustrate the general concept.
Accessory Obligations
In addition to the calculation, companies must comply with ancillary obligations, such as eSocial, in order to correctly meet legal requirements.
It is essential to consult up-to-date legislation and, if necessary, enlist the help of an accountant to ensure correct compliance with social security obligations.
What are the INSS contribution rates?
INSS (National Social Security Institute) contribution rates in Brazil vary according to the salary range of workers. Currently, the table of progressive INSS rates is organized as follows:
Up to one minimum wage (R$ 1,100.00): 7.5%
From one minimum wage (R$ 1,100.00) to the INSS ceiling (R$ 6,911.11): 9%
From R$ 6,911.12 to R$ 13,822.24: 12%
These rates are applied to the worker's contribution salary, which is the amount used as the basis for calculating the social security contribution. It is worth mentioning that there is a maximum ceiling for the contribution salary, which is updated annually.
It is important to note that these rates relate to the contribution of the insured person (worker) and do not include the employer's contribution, which is the responsibility of companies and has specific rates.
In addition, the Pension Reform was enacted in November 2019 (Constitutional Amendment 103/2019)This legislation brought about changes to the INSS contribution rates and established transitional rules. We recommend checking the updated legislation or consulting an accounting professional for specific and up-to-date information.
Example calculation for different salary bands
Let's calculate the social security contribution (INSS) for different salary brackets using the rates in force. Remember that the values in the minimum wage table and the INSS ceiling refer to the year 2022, and these figures may be updated annually.
Example calculations:
R$ salary 1,000.00
Rate: 7.5%
Contribution: R$ 1,000.00 * 7.5% = R$ 75.00
R$ Salary 3,000.00
Rate: 9%
Contribution: R$ 3,000.00 * 9% = R$ 270.00
R$ Salary 5,000.00
Rate: 9%
Contribution: R$ 5,000.00 * 9% = R$ 450.00 (up to the INSS ceiling)
R$ salary 10,000.00
Rate: 12%
Contribution: R$ 10,000.00 * 12% = R$ 1,200.00 (INSS ceiling)
Comments:
For salaries above R$ 6,911.12, the rate of 12% is applied to the part of the salary that exceeds this amount up to the INSS ceiling.
The table serves as a simplified example and does not include other details, such as possible deductions.
The Social Security Reform introduced changes to tax rates and established transition rules. Consult updated legislation or an accountant for specific and up-to-date information.

Payment of employer's INSS
Companies are obliged to pay the INSS Patronal, which is the social security contribution relating to employees' payroll. This contribution is calculated on salaries and other remuneration.
Issuing Collection Notes
It is the entrepreneur's responsibility to issue the social security contribution forms using the systems provided by the government, such as eSocial.
Calculation and Payment of Third Party Contributions
In addition to the INSS Patronal, companies may have obligations to contribute to other bodies or entities, such as Sistema S (Senai, Sesi, Senac, etc.), INCRA and salário-educação. The entrepreneur must calculate and pay these contributions where applicable.
Submission of Information to eSocial
eSocial is a government platform that brings together labor, social security and tax information. Entrepreneurs must regularly feed eSocial with data relating to employees and their remuneration.
Respect for the Rates and Tables in Force
It is essential that the entrepreneur is up to date on the rates and tables in force, as these can change over time.
Debt settlement
If the company has social security debts, they must be settled, either through installments or other forms of negotiation offered by the competent bodies.
Attention to Legislative Changes
Social security legislation can change, and entrepreneurs must be aware of these changes in order to adjust their practices in line with the new requirements.
Documentation maintenance
The company must keep the documentation relating to payroll and social security contributions in order, as it may be requested in the event of any inspections.
It is recommended that entrepreneurs rely on the advice of specialized accounting professionals to ensure correct compliance with all INSS-related obligations.
Which declarations and payments are mandatory?

Obligations in relation to INSS (National Institute of Social Security) in Brazil involve a number of mandatory declarations and payments by companies. Below are some of the main ones:
eSocial
eSocial is an integrated system that unifies the provision of information on tax, social security and labor obligations. Companies must feed eSocial with data such as payroll, information on employees, social security contributions, among others.
GFIP (Service Time Guarantee Fund and Social Security Information Collection Form)
The GFIP is a statement that contains information on workers' pay and other social security and tax information. It is used to pay the INSS Patronal.
DCTFWeb (Statement of Federal Social Security Tax Debts and Credits and those of Other Entities and Funds)
DCTFWeb is used to declare federal tax debts and credits, including social security contributions. It replaces the GFIP for most companies.
GPS (Social Security Guide)
The GPS is the payment form for social security contributions. It contains the amounts owed to the INSS Patronal, as well as the contributions of the insured.
DIRF (Withholding Income Tax Return)
The DIRF is an annual declaration containing information on income paid to individuals and companies. It includes data on INSS withholdings made at source.
PerdComp (Electronic Request for Refund, Reimbursement or Reimbursement and Declaration of Compensation)
PerdComp is used to offset social security credits, such as amounts paid unduly or in excess.
DACON (Statement of Calculation of Social Contributions)
DACON was a declaration used to calculate social contributions, including the INSS, but it has been replaced by obligations such as DCTFWeb.
Consultation of social security debts
Companies must regularly consult and settle any social security debts through the Federal Revenue Service.
These are some of the main obligations related to the INSS, but it is essential that companies are up to date with current legislation and regulatory changes. Relying on the advice of accounting professionals is crucial to ensuring correct compliance with these obligations.
INSS benefits for employees: How does this impact the company?
INSS (National Social Security Institute) benefits for employees are an essential part of the Brazilian social security system. They aim to ensure social protection for workers in situations such as illness, accidents, retirement, among others. The impact of these benefits on companies is significant and can manifest itself in various ways:
Labor charges
Companies are responsible for paying their employees' social security contributions, which is a labor burden. This involves payroll deductions and employer contributions.
Costs of sick leave and accidents
In cases of absence due to illness or accident, INSS benefits come into play. For companies, this can mean additional costs, especially if there are no internal policies for supplementing salaries during the period of absence.
Maternity and Paternity Leave
Maternity and paternity leave are INSS benefits that guarantee protection for employees during these special times. Companies can feel the impact, especially in sectors where the temporary absence of employees can affect productivity.
Retirement
Retirement is an INSS benefit that can have an impact on a company's workforce. The departure of more experienced professionals may require succession and training strategies to ensure continuity of operations.
Benefits as a Competitive Differential
Offering employees an environment that values and facilitates access to INSS benefits can be perceived as a competitive advantage by the company. This contributes to satisfaction and talent retention.
Indirect costs
The country's economic instability and changes in social security legislation can indirectly impact companies, influencing strategic decisions, budget adjustments and human resources policies.
Impact on Productivity and Employee Health
Ensuring employees have access to INSS benefits can have a positive impact on the overall health and productivity of the team, reducing absenteeism due to untreated health issues.
In short, INSS benefits have significant implications for companies' operations and strategies. Understanding and properly managing these aspects is essential for the smooth running and financial balance of organizations.
The INSS (National Social Security Institute) offers a variety of benefits to Brazilian workers, with the aim of providing social protection in various situations throughout life. Below is an overview of the main benefits offered by the INSS:
Age pension: Aimed at urban and rural workers who reach the minimum age stipulated by law.
Retirement for Length of Service: Aimed at those who have reached the minimum social security contribution time.
Disability pension: Granted to workers who become permanently unfit for work.
Sick pay: For insured people who are temporarily unable to work due to illness or accident.
Accident benefit: Paid to workers who suffer an accident and are left with sequelae that reduce their ability to work.
Maternity pay: Granted to pregnant insured women, adopters, and in cases of legal guardianship for adoption.
Family allowance: Benefit paid to low-income insured people with children up to the age of 14 or disabled.
Death pension: Granted to the dependents of the deceased insured person, varying according to the insured person's category and contribution time.
Retention Allowance: Benefit paid to the dependents of a low-income insured person in prison.
Inclusion aid: Intended for insured persons who, after being granted sickness benefit, remain incapacitated and need permanent assistance from another person.
Continuous Cash Benefit (BPC): It offers a monthly minimum wage to elderly people over 65 or people with disabilities who can prove they have no means of supporting themselves.
These benefits make up the INSS social protection structure, providing financial support in various circumstances throughout the life of the worker and their dependents. It is important to note that eligibility for each benefit is subject to specific criteria established by social security legislation.
Social security contributions are mandatory labor charges that affect the cost of labor for companies. Understanding and properly managing these charges is essential for organizations' financial planning.
Labor charges: Social security contributions are mandatory labor charges that affect the cost of labor for companies. Understanding and properly managing these charges is essential for organizations' financial planning.
Leave of absence costs: Benefits such as sick pay and maternity pay can result in additional costs for companies, especially if there are no internal policies to supplement salaries during periods of absence.
Productivity and Operational Continuity: Sick or accident leave can have an impact on productivity and operational continuity. Companies must develop strategies to minimize these impacts, such as implementing occupational health programs.
Personnel and Succession Planning: The retirement of workers can require efficient personnel planning, ensuring continuity of operations and avoiding skills gaps. Knowledge about employees' eligibility for pension benefits is crucial in this context.
Human Resources Policies: Companies can use benefits as a competitive differentiator to attract and retain talent. Offering social benefits has an impact on employee satisfaction and loyalty.
Legal Aspects and Compliance: Managing INSS benefits involves complex legal aspects. Keeping up to date with regulations is crucial to ensuring compliance with social security legislation.
Tax planning: Social security charges are part of the tax cost for companies. Proper tax planning can help optimize these costs and ensure compliance with tax obligations.
Well-being and Organizational Culture: Companies that show concern for their employees' well-being by offering support in health situations can promote a positive organizational culture and strengthen relationships with employees.
Additional Benefits Strategies: Companies can consider additional benefit strategies, such as supplementary insurance, to mitigate financial risks related to unforeseen events, such as accidents or serious illnesses.
In summary, the effective management of INSS benefits is fundamental for companies, directly impacting financial, operational and cultural aspects. Successful companies integrate a comprehensive approach to managing these benefits, in line with their organizational strategies and values.
The individual entrepreneur, also known as an individual entrepreneur with unlimited liability, is a business format in which the owner is solely responsible for the enterprise and is unlimitedly liable for its debts. In the context of INSS (National Institute of Social Security)The individual entrepreneur is subject to some specific rules regarding social security contributions. Here are the main points about how the INSS works for individual entrepreneurs:
INSS contribution
Individual entrepreneurs are responsible for making their own social security contributions to the INSS. This is done by paying a rate on the contribution salary, which is calculated on the basis of the remuneration the entrepreneur earns each month.
Contribution Calculation Basis
The calculation basis for the individual entrepreneur's social security contribution is your pro-labourThis is the remuneration paid to oneself. Pro-labore must be defined by the entrepreneur, taking into account the legislation and the company's financial conditions.
Contribution rates
INSS contribution rates can vary depending on the salary range of the individual entrepreneur. It is important to be aware of the rates in force in order to calculate the contribution correctly.
Social Security Benefits
By contributing regularly, the individual entrepreneur is entitled to the social security benefits offered by the INSS, such as old-age retirement, sick pay, maternity pay, among others. The granting of these benefits is conditional on meeting the requirements established by social security legislation.
Accessory Obligations
In addition to the social security contribution, individual entrepreneurs must also comply with ancillary obligations, such as submitting declarations and documents required by the INSS. Failure to comply with these obligations can result in penalties.
Tax planning
Individual entrepreneurs should consider tax planning strategies to optimize their tax burden. This may involve making the right choice of pro-labour and looking for tax benefits provided for in the legislation.
Accounting Advice
Given the complexity of social security and tax rules, it is highly recommended that individual entrepreneurs rely on the advice of an accounting professional. This support helps them comply with legal obligations and optimize tax aspects.
In short, the individual entrepreneur needs to understand the responsibilities and obligations related to social security contributions to the INSS in order to guarantee the regularity of their social security situation and access to the benefits offered by social security.
Specific features of the individual entrepreneur's contribution
The individual entrepreneur's contribution to the INSS has some specific characteristics that need to be taken into account in order to guarantee correct payment and compliance with social security obligations. Below are some specific characteristics of this contribution:
Calculation Basis - Pro-Labore
The calculation basis for the individual entrepreneur's social security contribution is the pro-labore, which represents the remuneration that the entrepreneur pays himself for his work in the company. It is on this amount that the contribution rate will be levied.
Progressive rates
The contribution rates for individual entrepreneurs can vary according to salary range. They follow a progression, with lower rates for lower salaries and higher rates for higher salaries.
Contribution Ceiling
Like other individual taxpayers, individual entrepreneurs are subject to the Social Security ceiling, i.e. the contribution is calculated up to a certain limit, even if the pro-labore is higher than this amount.
Self-declaration of Remuneration
The individual entrepreneur is responsible for self-declaring his or her remuneration, stating the amount of the pro-labore used as the basis for calculation. This declaration is essential for the correct payment of contributions.
Retirement and Social Security Benefits
Regular contributions ensure that the individual entrepreneur is entitled to retirement and other social security benefits offered by the INSS, as established by social security legislation.
Accessory Obligations
Individual entrepreneurs must comply with ancillary obligations, such as submitting declarations and documents required by the INSS. These obligations are essential for maintaining social security regularity.
Accounting Advice
Given the complexity of the social security rules, it is advisable to rely on the support of a specialized accounting professional. This professional can advise on the best way to make contributions and ensure that all legal obligations are met.
In short, understanding the specifics of the individual entrepreneur's contribution to the INSS is crucial to ensuring compliance with social security legislation and guaranteeing access to the social security benefits offered by the system.
[Article]: CLT vs. PJ: how should your company hire?
Differences from companies with employees
Companies made up of individual entrepreneurs have some significant differences from companies that have employees, especially with regard to labor and social security obligations. Here are some important distinctions between these two situations:
Number of people involved
Individual entrepreneurs are usually sole proprietors, responsible for the management and operation of the business. On the other hand, companies with employees involve hired staff in addition to the entrepreneur.
Labor obligations
Individual entrepreneurs are not obliged to follow all the labor rules that apply to employers with teams of employees. This includes issues such as working hours, paid vacations and other labor rights that apply specifically to employees.
Social Security Responsibilities
While individual entrepreneurs are responsible for contributing to the Social Security system, taking their pro-labour as the basis for calculation, companies with employees must make social security contributions for both the employer and the employees.
Social charges
Companies with employees have additional social charges, such as the Severance Indemnity Fund (FGTS) and the payment of benefits such as transport vouchers and meal vouchers. Individual entrepreneurs are exempt from these specific obligations.
Labor relations
Companies with employees need to manage more complex employment relationships, involving employment contracts, internal policies, performance appraisals and so on. Individual entrepreneurs deal mainly with their own activities and not with a team of employees.
Human Resources Planning
Companies with employees need to develop human resources planning strategies, taking into account hiring, firing, training and professional development. For individual entrepreneurs, the focus is on their own management and development.
Work environment
The work environment for individual entrepreneurs often consists of their own workspace, while companies with employees need to provide a suitable environment for the team, meeting safety and comfort standards.
Labor benefits
Companies with employees can offer a variety of benefits, such as health insurance, life insurance and private pension plans, as a way of attracting and retaining talent. Individual entrepreneurs generally don't have the same range of benefits to offer themselves.
[Article]: Understand the importance of Vacation Control
Delays and debts with the INSS: What are the consequences for the company?
Delays and debts with the INSS (National Social Security Institute) can lead to various consequences for the company, ranging from financial issues to legal penalties. Here are some of the main consequences:
Fines and Interest
A company that fails to pay its social security contributions on time will be subject to fines and interest on the amount due. These additional charges can be a significant financial burden.
Protest and Tax Enforcement
Failure to pay social security contributions can lead to the company's debt being registered as an active debt. This allows the Federal Revenue Service to initiate judicial collection through tax enforcement, which can result in the seizure of assets and the blocking of bank accounts.
Impediments and Restrictions
Companies with debts to the INSS can face restrictions on their activities, such as the impossibility of taking part in public tenders, obtaining negative debt certificates, or even having difficulties in carrying out financial transactions.
Accountability of Managers
In cases of social security debts, the managers and people responsible for the company can be held liable. This includes the possibility of them being personally liable for the debts and being subject to legal action.
Exclusion from Installment Payments
If the company has opted to pay its debts to the INSS in installments and fails to comply with the established conditions, it may be excluded from the installment plan and subject to the legal and financial consequences mentioned above.
Review of Social Security Benefits
A company that fails to pay its contributions correctly can have a direct impact on workers' social security benefits. A review of these benefits can be a consequence, generating additional burdens for the company.
Repercussions on the Company's Image
Delays and debts with the INSS can have an impact on the company's reputation, affecting its image with clients, suppliers and employees. Failure to comply with tax obligations can lead to mistrust and damage relationships with stakeholders.
To avoid these consequences, it is essential that the company maintains efficient financial management, complies with social security obligations and, in the event of difficulties, seeks to regularize the situation through negotiations or installments offered by the competent bodies. The support of specialized accounting and legal professionals is crucial to guaranteeing compliance with legal obligations and preserving the company's financial health.
[Article]: LGPD and Human Resources: what changes?
Non-payment or late payment of legal obligations, such as social security contributions to the INSS, can have various legal and financial consequences for a company. Here are some of the main ones:
Fines and Interest
The company is liable to pay fines and interest for late or non-payment of social security contributions. These additional charges can represent a significant financial burden.
Registration in Active Debt
Failure to pay social security contributions can lead to the debt being registered as an active debt. This allows the Federal Revenue Service to initiate judicial collection by means of tax enforcement.
Asset seizure
In more serious cases, the company may have its assets seized as a way of guaranteeing payment of the debt. This includes the possibility of seizing bank accounts and other assets.
Protests and Restrictions
The company can have its name protested and face restrictions on its activities, such as the impossibility of participating in public tenders and obtaining negative debt certificates.
Accountability of Managers
The managers and people in charge of the company can be held personally responsible for the social security debts, being legally liable and subject to legal action.
Exclusion of Tax Benefits
Companies in default can be excluded from tax benefits and government incentives, which has a negative impact on their tax burden.
Review of Social Security Benefits
Delinquency can result in a review of the social security benefits granted to workers, with possible adjustments and corrections.
Image and Reputation
Failure to comply with tax obligations can affect the company's image and reputation, damaging relationships with customers, suppliers and employees.
Exclusion from Installment Payments
If the company has opted to pay its debts in installments and fails to comply with the conditions laid down, it may be excluded from the installment plan and subject to all the consequences mentioned above.
To avoid these consequences, it is essential that the company maintains efficient financial management, complies with its tax and social security obligations, and seeks to regularize the situation when necessary. The support of specialized accounting and legal professionals is essential to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with legal obligations.
[Article]: Digital FGTS has revolutionized the management and payment of the benefit!
Strategies for settling debts
Settling debts with the INSS and other social security agencies can be challenging, but it is crucial to avoid legal and financial consequences. Here are some strategies that companies can adopt to regularize their debts:
Friendly negotiation
Contacting the INSS to negotiate amicably is the first step. It is often possible to establish payment agreements, installments or even obtain discounts on fines and interest.
Installment payment of debts
Checking the possibility of paying off overdue debts in installments is a common strategy. Installments allow the company to pay off its debts more gradually, relieving financial pressure.
Use of negative certificates
Regularizing debts is essential for obtaining negative debt certificates. These certificates are often required in bidding processes and are essential for the company's fiscal regularity.
Taking advantage of Regularization Programs
Paying attention to tax regularization programs offered by the government can be an opportunity to settle debts with special conditions, such as discounts on fines and interest.
Financial Analysis and Planning
Carrying out an in-depth financial analysis can help identify the source of problems and implement measures to avoid future delays. Sound financial planning is essential.
Accounting and legal advice
Relying on the advice of accounting and legal professionals who specialize in social security issues is crucial. They can advise on the best ways to regularize and ensure compliance with legislation.
Evaluation of Tax Benefits
Exploring the possibility of using tax benefits provided for in specific legislation can be a strategy for reducing the impact of debts on the tax burden.
Constant monitoring
After regularization, it is important to keep a constant eye on social security obligations. An efficient control and monitoring system prevents further problems in the future.
Remember that the ideal approach may vary according to the company's specific situation. Consulting specialized professionals is essential to making informed decisions and ensuring that the strategy adopted is the most appropriate for settling social security debts.
[Article]: Find out how notice works
Conclusion
In conclusion, the proper management of social security obligations, such as contributions to the INSS, is fundamental to companies' financial health and tax compliance. CLM Controller stands out as a specialist in this service, offering accounting and legal expertise to help companies comply with their social security obligations.
With a qualified and experienced team, CLM Controller not only provides support in settling debts and negotiating with social security agencies, but also offers customized solutions for the efficient management of contributions, minimizing risks and ensuring compliance with current regulations.get to know CLM Controller's solutions now.